What is Thermal Power?
It is the process of generating electricity by converting heat energy into mechanical energy. This process is typically achieved through the use of steam turbines, which are powered by steam that is created by heating water to its boiling point.
What energy sources can be used for thermal power?
There are several types of energy sources that can be used. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, are commonly used to produce thermal power. Fossil fuels are burned in a furnace to generate heat, which is then used to create steam that powers a turbine.
Nuclear energy is another source. In a nuclear power plant, nuclear reactions are used to generate heat, which is then used to create steam that powers a turbine. Nuclear power plants are capable of generating large amounts of electricity, but they also present unique challenges, such as nuclear waste disposal and the risk of accidents.
Renewable energy sources, such as biomass and geothermal energy, can also be used. Biomass power plants burn organic material, such as wood or agricultural waste, to create heat, which is then used to generate steam. Geothermal power plants harness the natural heat from the earth’s core to generate steam that powers a turbine
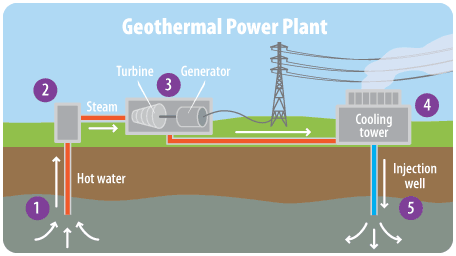
The image below shows the process to generate Geothermal Power.
Advantages and disadvantages of thermal power.
One of the advantages is that it can be generated on demand, which makes it a reliable source of electricity. However, thermal power also has some disadvantages. For one, it is a non-renewable source of energy, meaning that it depletes over time. Additionally, the process of generating it can produce greenhouse gases, which contribute to climate change.
Despite these drawbacks, thermal power remains an important source of electricity generation in many parts of the world. Governments and businesses continue to invest in power plants to produce energy from heat both to meet the increasing demand for electricity and to replace aging power plants that are reaching the end of their operational life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, thermal power is the process of producing electricity by converting heat energy into mechanical energy. This process can be based on a variety of energy sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources. While there are advantages, such as its ability to generate electricity on demand, it also has some drawbacks, such as its contribution to climate change. As the world’s energy needs continue to grow, it will be important to consider a mix of energy sources, including thermal power, to meet the demand for electricity in a sustainable way.
Frequently asked questions
How is thermal power generated?
Thermal power is generated by converting heat energy into mechanical energy through the use of steam turbines, which are powered by steam that is created by heating water to its boiling point.
What are the energy sources used for thermal power generation?
Fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, nuclear energy, and renewable energy sources such as biomass and geothermal energy can be used to generate thermal power.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of thermal power?
One of the advantages of thermal power is that it can be generated on demand, which makes it a reliable source of electricity. However, thermal power is a non-renewable source of energy, depletes over time, and contributes to climate change due to the production of greenhouse gases.